| Key
Facts |
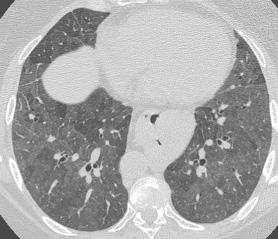
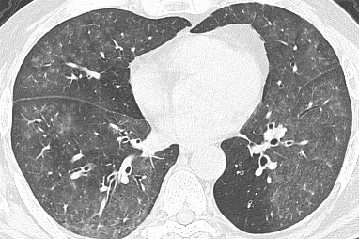
- Nonspecific finding seen in the majority of diffuse lung diseases
- Often an early sign or less severe sign of diffuse lung diseaseClassically associated with air bronchograms
- Lung increased opacification but not to the extent of obscuring blood vessels
- Pathologic correlates nonspecific: normal expiration, interstitial thickening, airspace filling, or partial collapse ie. any interstitial, airsapce or cause of atelectasis
- Best area of lung to biopsy or serially follow to determine affects of therapy
|
| Pattern |
- Associated findings or nodules, cysts, or septal thickening often helpful in differential
|
| Differential
Diagnosis |
- ABC's
- Alveolar proteinosis
- ARDS
- Blood
- BOOP
- CMV
- Contusion
- Drug toxicity
- DIP
- Eosinophilic pneumonia
- Edema
- Fibrosis
- Granulomatous disease
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
|
| References |
Collins J, Stern EJ. Ground-glass opacity at CT: The ABCs. AJR 169: 355-367, 1997.
|