| Key
Facts |
- Unknown cause with
poor prognosis
- Heterogenous fibrosis
primarily in the periphery lower lobes
- Honeycombing and
traction bronchiectasis at HRCT
|
| Imaging
Findings |
Chest
radiograph
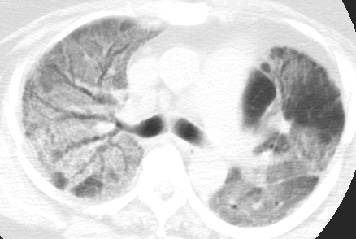
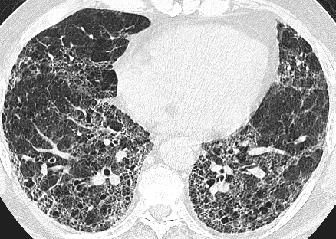
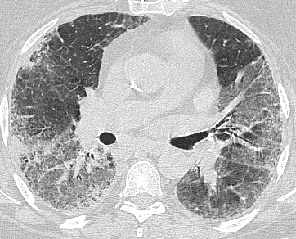
- Best imaging clue:
Basilar peripheral honeycombing and volume loss
- Irregular linear
opacities in contrast to the granulomatous diseases which are primarily
nodular
- Chest radiography
may be normal in spite of symptoms
CT/HRCT
- Useful to plan
biopsy
- Spectrum from ground
glass opacites to honeycombing
- Traction bronchiectasis
required for confident radiographic diagnosis
- CT may be normal
in mild (or early) disease
- Subpleural distribution
in 80%
- Mediastinal nodes
may be mildly enlarged (nodes < 2 cm diameter)
|
| Differential
Diagnosis |
- Asbestosis
- BOOP
- Drug reaction
- Chronic hypersensitivity
reaction
- Sarcoidosis
|
| Pathological
Features |
- Unknown insult
to alveolar wall and interstitium
- UIP thought to
be repetitive insult vs AIP
- Usually inhomogeneous
both spatially and temporally
- Fibroblast proliferation
|
| Clinical
Presentation |
- Progressive dyspnea,
dry cough and fatigue
- 5th-7th decade,
slight predominance in men
- Treatment
- Survival
|
| References |
Hansell
DM: Computed tomography of diffuse lung disease: Functional correlates.
Eur Radiol 11:1666-80, 2001
|